 |
| Education & Health |
Health education is a profession of educating people about health. Areas within this profession encompass environmental health, physical health, social health, emotional health, intellectual health, spiritual health, and sexual and reproductive health education.
Health education can be defined as the principle by which individuals and groups of people learn to behave in a manner conducive to promoting, maintaining or restoration of health. However, as there are multiple definitions of health, there are also numerous definitions of health education. In America, the Joint Committee on Health Education and Promotion Terminology of 2001 defined Health Education as "any combination of planned learning experiences based on sound theories that provide individuals, groups, and communities the opportunity to acquire information and the skills needed to make quality health decisions."
The World Health Organization defined Health Education as "compris[ing] [of] consciously constructed opportunities for learning involving some form of communication designed to improve health literacy, including improving knowledge, and developing life skills which are conducive to individual and community health.
Role of the Health Education Specialist
From the late nineteenth to the mid-twentieth century, the aim of public health was controlling the harm from infectious diseases, which were largely under control by the 1950s. By the mid-1970s, it was clear that reducing illness, death, and rising health care costs could best be achieved through a focus on health promotion and disease prevention. At the heart of the new approach was the role of a health educator.
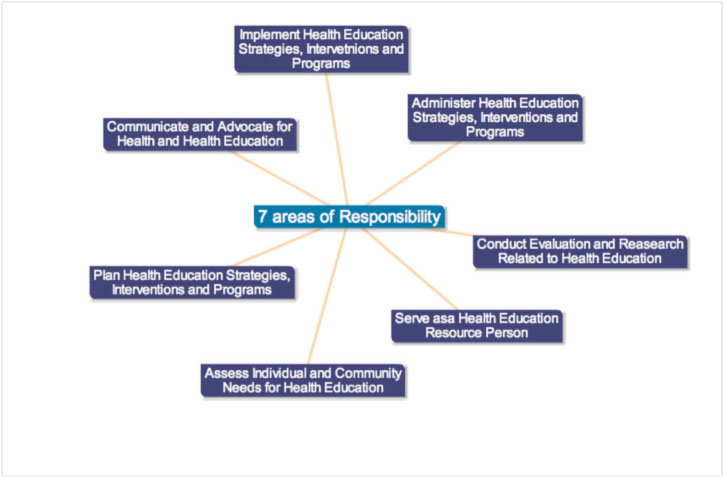
A health educator is "a professionally prepared individual who serves in a variety of roles and is specifically trained to use appropriate educational strategies and methods to facilitate the development of policies, procedures, interventions, and systems conducive to the health of individuals, groups, and communities" (Joint Committee on Terminology, 2001, p. 100). In January 1978, the Role Delineation Project was put into place in order to define the basic roles and responsibilities for the health educator. The result was a Framework for the Development of Competency-Based Curricula for Entry Level Health Educators (NCHEC, 1985). A second result was a revised version of A Competency-Based Framework for the Professional Development of Certified Health Education Specialists (NCHEC, 1996). These documents outlined the seven areas of responsibilities, which are shown below. The Health Education Specialist Practice Analysis (HESPA II 2020) produced "a new hierarchical model with 8 Areas of Responsibility, 35 Competencies, and 193 Sub-competencies".
Health education has evolved into health promotion. Health education is any combination of learning experiences designed to facilitate voluntary actions conducive to health. Health promotion is the combination of educational and environmental supports for actions and conditions of living conducive to health, thereby including health education. Four other main developments are relevant: the need for planning (the PRECEDE–PROCEED model), the importance of evaluation, the use of social and behavioral science theories in the development of health promotion interventions (the Intervention Mapping process). Finally, recent developments in information technology (e.g., computer tailoring) and their effect on health promotion are presented.


Post a Comment